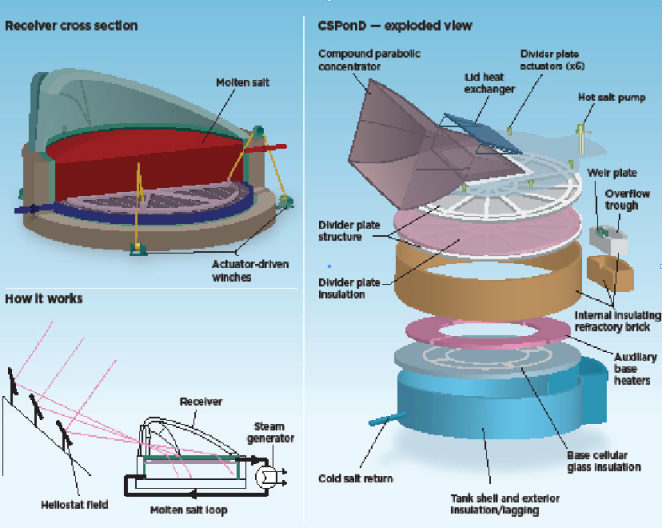
Like existing CSP power-tower developments, the MIT concept uses an array of mirrors, called heliostats, to reflect sunlight onto a receiver that powers steam turbines.
But instead of mounting the reflectors on the ground to concentrate sunlight up to a receiver tower, the design would spread the heliostats across a hillside, directing the insolation into a roofed vat of molten salt acting as receiver and energy storage reservoir.
The